Aminoglycosides Act Through Which of the Following Mechanisms
Aminoglycosides are a group of potent antibiotics primarily used to treat certain infections caused by aerobic Gram-negative bacteria. Today there are several other aminoglycosides.

Aminoglycosides Mechanism Of Resistance
C Transpeptidation linking and maturation.
. There are three mechanisms of aminoglycoside resistance. Which of the following is correct concerning whether this patient should be started on aminoglycosides. This impairment causes mismatches between codons and anticodons resulting in the production of proteins with incorrect amino acids and shortened proteins that insert into the cytoplasmic membrane.
Aminoglycosides are selectively active against oxygen-dependent aerobic gram-negative bacterial cells since these cells possess the chemical characteristics that attract aminoglycosides and the specific transport mechanisms that facilitatethe uptake of the drugs into the cells. Aminoglycosides are potent broad-spectrum antibiotics that act through inhibition of protein synthesis. Causes mismatches between codons and anticodons leading to faulty proteins that insert into and disrupt cytoplasmic membrane.
Aminoglycosides are a class of antibiotics used mainly in the treatment of aerobic gram-negative bacilli infections although they are also effective against other bacteria including Staphylococci and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Among various bacterial species resistance to AGs arises through a variety of. Antibiotic mechanisms of action target all the following except.
They are used in the treatment of severe infections of the abdomen urinary tract skin and soft tissue bone cervix blood eye ear lungs and heart. Amikacin gentamicin kanamycin neomycin and tobramycin. Reduced uptake or decreased cell permeability alterations at the ribosomal binding sites or production of aminoglycoside modifying enzymes.
You must c C reate. Several features of these mechanisms are of clinical significance. Aminoglycosides and glycopeptidians b.
Welcome to your Aminoglycosides Quiz. Mechanism of Action The aminoglycosides are bactericidal antibiotics and all having same general pattern of action. Aminoglycosides act through which of the following mechanisms.
D Synthesis of precursors in the cytoplasm. Aminoglycosides are used for broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy and have a narrow therapeutic range. Renal damage is a potential adverse effect of aminoglycosides.
Asked Apr 23 2021 in Biology Microbiology by rjf0401. The class has been a cornerstone of antibacterial chemotherapy since streptomycin was first isolated from Streptomyces griseus and introduced into clinical use in 1944Several other members of the class were introduced over the intervening years including neomycin. The highest therapeutic blood.
B Insertion of glycan units into the cell wall. Those that a bacterium acquires through plasmids. The aminoglycosides directly target which structure of the bacterial cell.
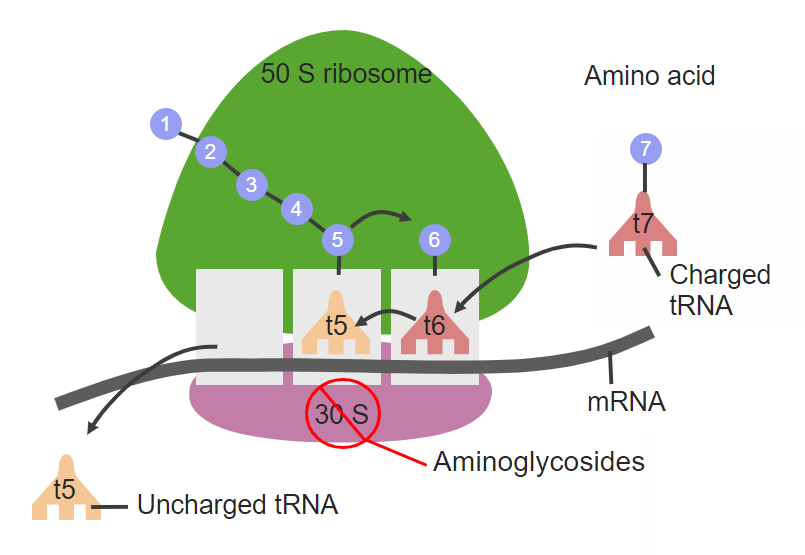
Aminoglycosides are large highly polar antibacterial drugs that bind to the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosomes impairing the proofreading ability of the ribosomal complex. What is aminoglycoside antibiotic. The mechanism of antibacterial action of tetracycline involves 111.
Mechanisms of Aminoglycoside Resistance. Aminoglycosides and quinolones c. Streptomycin gentamicin neomycin kanamycin.
Inhibition of the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol. But they act by inhibiting peptide elongation. Ataluren by inhibiting release factor-dependent termination of protein synthesis and G418 by.
A Transportation of lipid bound precursors across the cytoplasmic membranes. Aminoglycosides are potent broad-spectrum antibiotics that act through inhibition of protein synthesis. Aminoglycosides are amongst the most important compounds used to treat serious nosocomial infections caused by aerobic.
The aminoglycosides are broad-spectrum bactericidal antibiotics that are commonly prescribed for children primarily for infections caused by Gram-negative pathogens. 1 The antibacterial activity of the aminoglycosides depends on an effective concentration of antibiotic outside the cell. It is described in two ways 1.
Asked Apr 23 2021 in Biology Microbiology by rjf0401. 1 was first isolated from Streptomyces griseus and introduced into clinical use in 1944. Inhibition of DNA -.
Aminoglycoside AG antibiotics are used to treat many Gram-negative and some Gram-positive infections and importantly multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. This type of oxygen dependent transport system is absent in anaerobes. The most commonly used inhibitors of cell wall biosynthesis act on.
The class has been a cornerstone of antibacterial chemotherapy since streptomycin Fig. Aminoglycosides requires an active transport system oxygen dependent for the uptake of drugs inside bacterial cell. Aminoglycosides are poorly absorbed from the gut and must therefore be delivered via parenteral routes.
Macrolides and tetracyclines d. Transport of amino glycoside through the bacterial cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane depending upon polarity and oxygen dependent active process 2. Filariasis an infection which can lead to lymphatic obstructive disease is caused by Wuchereria bancrofti and Brugia malay.
2 Anaerobic bacteria and induced mutants are generally resistant because they lack appropriate transport systems. Aminoglycosides act primarily by impairing bacterial protein synthesis through binding to prokaryotic ribosomes. Mutation in the gene responsible for deletion or alteration of the receptor protein can also leads to development of resistance towards aminoglycosides.
Macrolides and quinolones. In general gentamicin tobramycin and amikacin. Aminoglycosides are thought to work by inhibiting protein.
Aminoglycosides act through which of the following mechanisms. And the aminoglycoside G418 employ orthogonal mechanisms in stimulating PSC read-through. They are often used in combination with other antibiotics.

Antibiotic Mechanisms Of Action Antibiotics Pharmacology Antibiotic Pharmacology

Aminoglycosides Concise Medical Knowledge

Antibiotic Classification Mechanism Basic Science Antibiotics Pharmacology Pharmacology Nursing Antibiotic

Comments
Post a Comment